Cardiac diagnostic… 2021 JVIM article
Title: Cardiac diagnostic test results and outcomes in 44 dogs naturally infected with Trypanosoma cruzi
Authors: Derek J. Matthews, Ashley B. Saunders, Alyssa C. Meyers, Sonya G. Gordon, and Sarah A. Hamer
Journal/Date of Publication: Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 2021
DOI: 10.1111/jvim.16166
Objective: To describe the cardiac diagnostic test results and outcomes of dogs naturally infected with T. cruzi.
Type of Study: Retrospective
Conclusions:
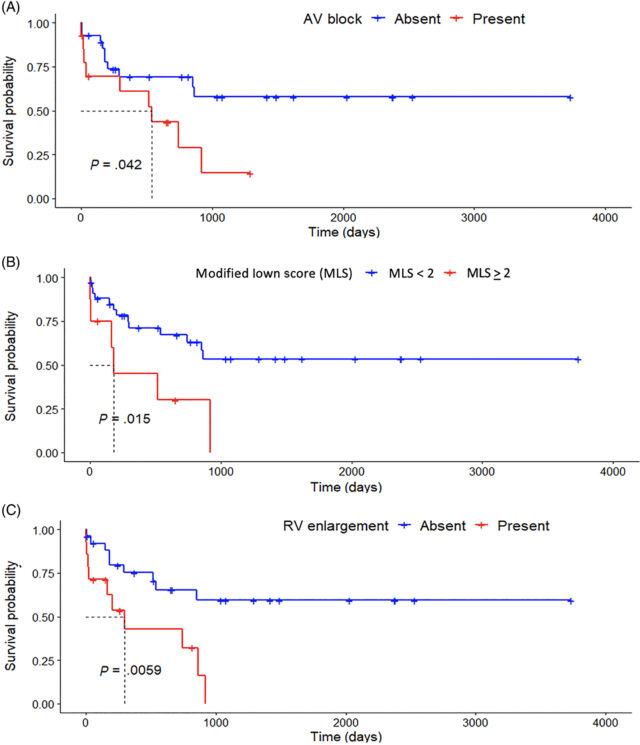
- ECG abnormalities were detected in 95% of the dogs, with ventricular arrhythmias (65%) and atrioventricular block (AVB, 33%) being common.
- Echocardiographic findings included right ventricular (RV) enlargement in 35% of dogs and left atrial enlargement in 29-49% depending on how measurements were obtained.
- Elevated cardiac troponin I (cTnI) concentrations were observed in 56% of dogs, indicating myocardial damage.
- Risk factors for cardiac-related death: RV enlargement, AVB, and high ventricular arrhythmia scores (modified Lown score ≥2) were associated with shorter survival times.
Clinical Application:
- ECG monitoring is critical for identifying arrhythmias and conduction abnormalities in T. cruzi-positive dogs.
- Ventricular arrhythmias (modified Lown score ≥2) and RV enlargement are strong indicators of poorer prognosis.
- Ambulatory ECG (Holter) can detect more severe arrhythmias missed by standard ECG.
- cTnI measurement can help assess myocardial damage, with high concentrations associated with heart damage.
- Echocardiography, particularly focusing on RV enlargement, provides prognostic information.
- Early identification of conduction abnormalities, such as AV blocks, provides evidence of infection.
- Close follow-up and comprehensive cardiac diagnostics (including ECG, echocardiography, cTnI) are useful tests when managing dogs with Chagas disease.