Climate Vulnerability Index Shows Where Action, Resources Are Needed To Address Climate Change Threats

Dr. Weihsueh Chiu, a professor at the Texas A&M School of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences, partnered with Environmental Defense Fund to create a new tool that provides communities and policymakers with actionable data about long-term vulnerabilities tied to climate change.
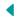
The Climate Vulnerability Index (CVI) is the most comprehensive screening tool of its type, showing how, why, and where climate risks threaten communities throughout the U.S.
“The launch of the CVI represents a significant leap forward in our understanding of the cumulative impacts of climate change,” Chiu said. “By offering a comprehensive framework to evaluate the multi-dimensional susceptibilities of communities to climate-related risks, this new tool provides a template for addressing local-scale climate and environmental justice around the globe.”
The CVI was based on the peer-reviewed journal article Characterizing vulnerabilities to climate change across the United States and was developed into an interactive map of the U.S. and dashboard by Darkhorse Analytics.
“The wildfire smoke from Canada and the heat wave over the entire Southern U.S. this summer emphasized the importance of better understanding the effects of climate change on people’s lives and of figuring out what we can do to help communities adapt to the changing conditions,” Chiu said.
How Does The CVI Work?
The CVI combines 184 sets of publicly available data to rank more than 70,000 U.S. census tracts. The data used can be grouped into seven broad domains — including health, infrastructure, and extreme events — which can then be broken down into sub-domains addressing specific issues like chronic disease and mental health.
“We first combined the data indicator sets at the most detailed level, then we combined those into the seven domains, and, finally, we combined those into the overall vulnerability index,” Chiu said. “This tool is designed to very quickly enable people to move from viewing the overall CVI score all the way down to a location’s score based on a single data indicator. This will help people identify potential connections, such as the interaction between infrastructure and flood risk.”
The CVI also allows users to search by location to view their overall climate vulnerability and the conditions that shape it — from quality of housing and access to supermarkets to proximity to toxic waste sites and number of deaths from air pollution.
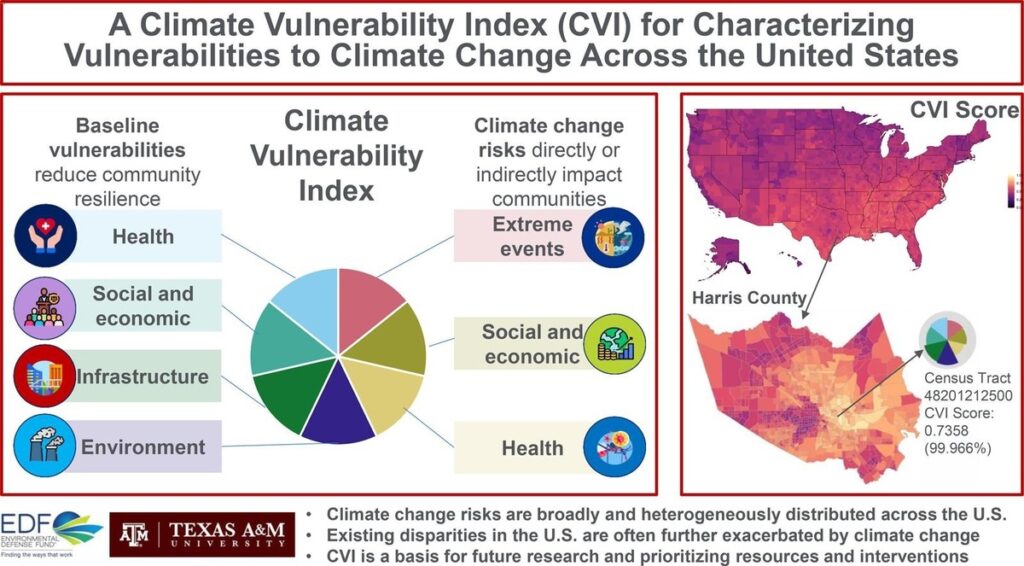
In Houston, for example, census tracts in the Settegast community northeast of downtown rank in the 99th percentile for overall vulnerability. The CVI shows what’s driving the vulnerability, including low chronic disease prevention, high exposure to harmful pollutants like soot, and inadequate access to fresh, nutritious food.
According to the CVI, these are the most vulnerable U.S. counties:
- St. John the Baptist, Louisiana
- Iberville, Louisiana
- Dillon, South Carolina
- Knox, Kentucky
- Tangipahoa, Louisiana
- St. Landry, Louisiana
- Acadia, Louisiana
- Floyd, Kentucky
- Talladega, Alabama
- Yazoo, Mississippi
The CVI will continue to be updated in the future to reflect the most recent census results and incorporate new data as it becomes available.
How Will The CVI Be Used?
The CVI equips and enables policymakers — and the advocates, community-based organizations, journalists, and academic researchers who hold them accountable — to use data to direct resources and action to areas of greatest need.
Alongside a comprehensive list of grant funding opportunities, user-friendly tutorials and real-life examples can be found on the CVI website to show how community advocates can use data for action.
“The Biden Administration has made a historic level of funding available to build toward climate justice and equity, but the right investments need to flow to the right places for the biggest impact,” said Dr. Grace Tee Lewis, senior health scientist at Environmental Defense Fund. “The CVI equips and enables communities, policymakers, and organizations to proactively address vulnerabilities and enhance resilience in the face of a changing climate.”
###
For more information about the Texas A&M School of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences, please visit our website at vetmed.tamu.edu or join us on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
Contact Information: Jennifer Gauntt, Director of VMBS Communications, Texas A&M School of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences; jgauntt@cvm.tamu.edu; 979-862-4216